What is Proof of Work (PoW)?

Proof of work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism used by the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, to secure and verify transactions. At heart, PoW is simply a computation designed to maintain data accuracy and protect the network while requiring participants known as miners.
This mechanism develops a private model where the participant’s objective is to solve various numeric problems. The first to come up with the right solution to that puzzle is allowed to append another new block of transaction to the blockchain and is paid for it.
In concept, PoW antedated cryptocurrencies and was initially employed in the contextual semantics of central computing specifications. It was first proposed by Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor in 1993 after they discovered a way to stop junk Emails by making the sender undertake a small task before sending the Email without a central authority.
In 2008, the owner of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto introduced PoW to create a trustless and decentralized consensus form of managing digital assets.
What Role Does Proof of Work Play in Cryptocurrencies?
Proof of work is the premise of several cryptocurrency systems given that they are used to verify transactions and maintain the blockchain.
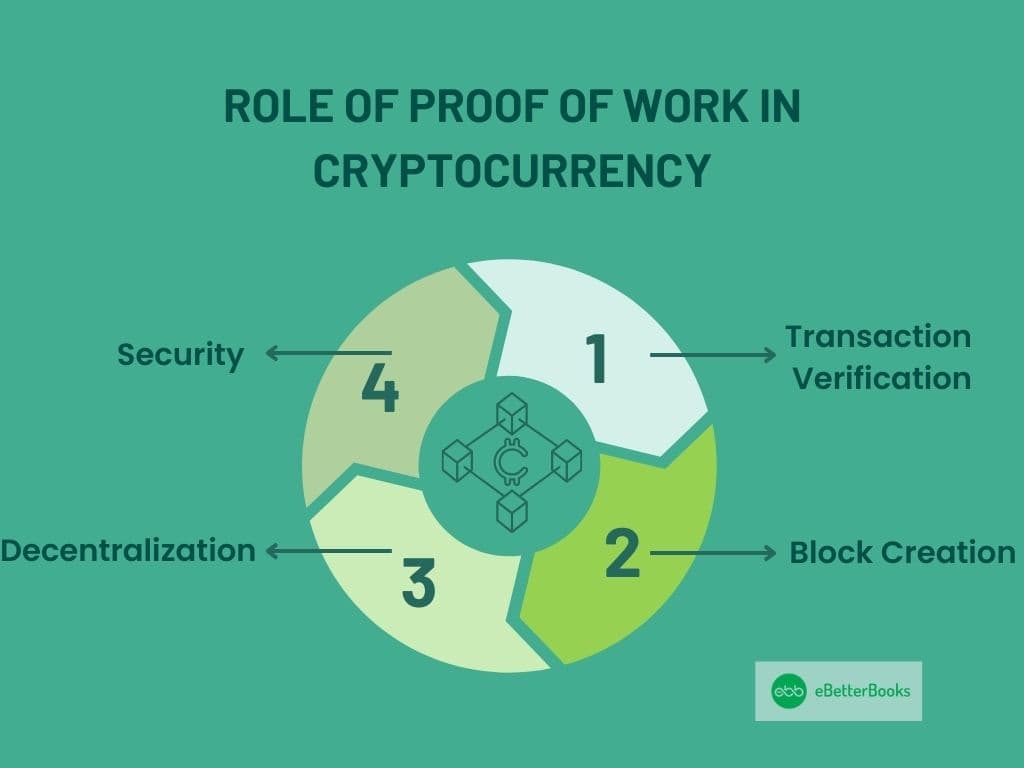
Its primary roles include:
- Transaction Verification: In virtual money like in Bitcoin, POW guarantees that such transactions are correct along with the avoidance of overspending, a foreign idea for traditional money but real for digital ones where the same can be spent more than once.
- Block Creation: In the Bitcoin system, miners package verified transactions into blocks and compete to solve complex mathematical problems. A block is created with transactions validated about it. Once it is created, it is added to the blockchain, thus forming a continuous and unalterable list.
- Decentralization: Technology achieves decentralization by providing a system where the power of making decisions is dispersed. Miners are decentralized and no single party can dominate the entire blockchain process.
- Security: POW hinders any wrong individual from making unnecessary attempts to compromise the network since the mining process is computation-intensive. Modifying the blockchain data would be prohibitive in terms of computational power, so attacks are out of the question.
It also brings the elements of scarcity and value into cryptocurrencies into existence. A lot of computing resources are needed to mine coins, and this makes the price or value of the currency to be determined by the number of people who want this cryptocurrency.
How Proof of Work Secures Bitcoin Transactions?
Bitcoin, the first digital currency and the most popular, employs PoW to guarantee the decentralized ledger’s security. Bitcoin mining is essentially a competition in which miners race to be the first to solve extremely complex cryptographic puzzles, enabling them to add the next block to the bitcoin blockchain and receive payment in the form of a new block of bitcoins.
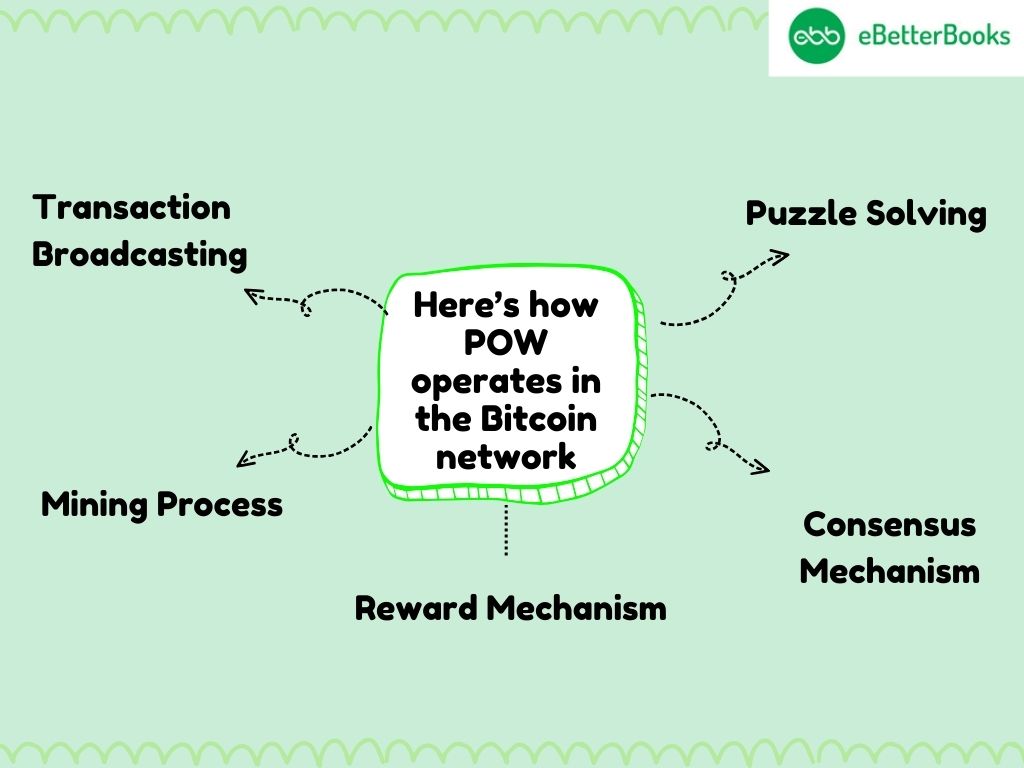
Here’s how POW operates in the Bitcoin network:
- Transaction Broadcasting: As a user sends bitcoins for a transaction, the transaction is relayed to the whole network and put in the memory pool which contains unconfirmed transactions.
- Mining Process: Miners choose several transactions from the memory pool and compile them in a candidate block. This is done by Decrypting a value from the block’s data to arrive at a cryptographic hash value below a targeted value. This procedure is rather time-consuming and involves the use of trial estimates.
- Puzzle Solving: The first one to successfully solve the alphanumeric code that comes with the transaction broadcasts the solution, or the proof of work, to the overall miners’ network. Other miners can check its accuracy, as in Bitcoin mining. If that is true, then the block is appended to the blockchain.
- Consensus Mechanism: Once the block is added to the blockchain all nodes in the network download the new copy of the blockchain to ensure that all nodes have an agreed blockchain.
- Reward Mechanism: The miner who is lucky to solve the above cryptographic puzzle earns a block reward in the BTC plus transaction fees from executed transactions.
Bitcoin transactions are secured by PoW since manipulating the blocks’ historical records becomes difficult computationally and financially.
To modify even a single transaction in a block, an attack would require the re-mining of not only the next block to the blockchain and valid block itself, but all blocks that follow it—a nearly impossible scenario requiring astounding amounts of computing power, time, and energy.
Benefits of Using Proof of Work (POW)
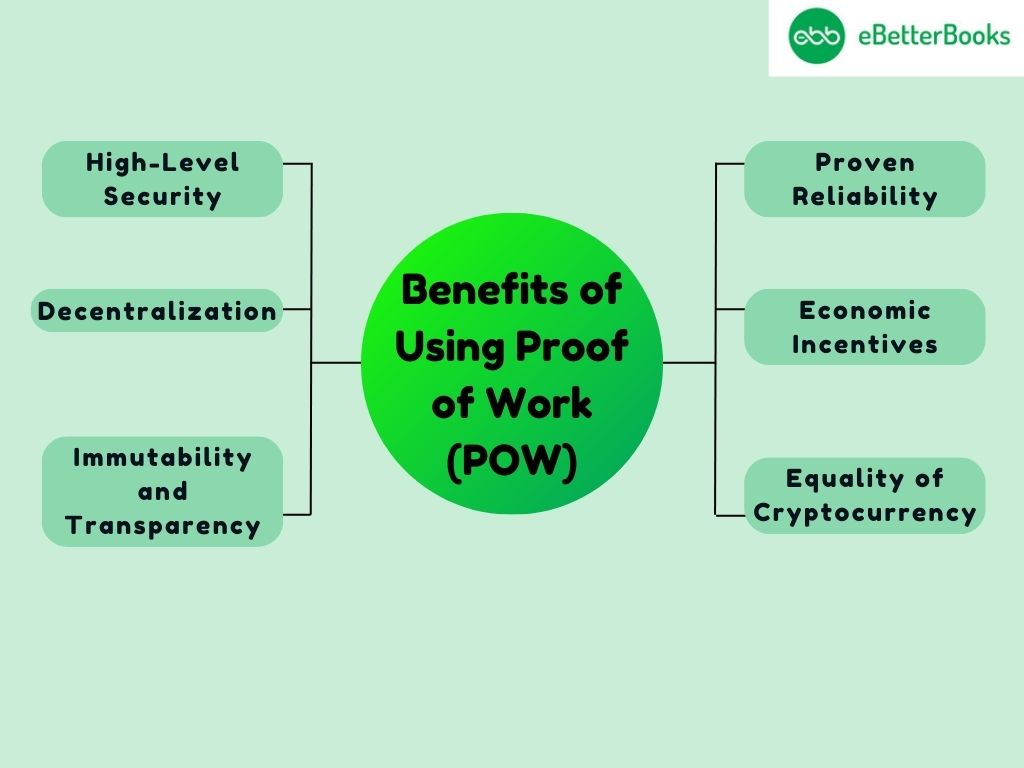
POW has proven to be a robust and effective consensus mechanism, offering several key benefits:
- High-Level Security: Through the explained PoW, blockchain networks are secured in a way that cannot be matched. The computational work involved in mining a block provides attackers with a very hard time altering the blockchain. For instance, a 51% attack holds that one entity possesses more than half of the computational power on the blockchain, which seems almost impossible in a large complex chain like Bitcoin.
- Decentralization: It should also be noted that control over the functioning of the PoW network is vested with miners. Open participation and no core hardware or software can be owned exclusively by central authorities or organizations, giving miners a chance to mine on their own. This self-organization is inherent to cryptocurrencies as a paradigm and makes it possible to develop trustless P2P interactions without agents.
- Immutability and Transparency: after a block is merged into the chain through the PoW approach, it becomes nearly impossible to change it. This immutability makes it possible that the transaction record is clear and cannot be altered all these make the users trust it.
- Proven Reliability: Integrated with Bitcoin since 2010, PoW has shown itself to be both credible and robust. Though Bitcoin core developers and other miners have tried to compromise the PoW mechanism several times, it has continued to thrive in the network’s integrity and solidity.
- Economic Incentives: Prospective of such Proof of Work motivates miners in the network with the provision of block rewards and transaction fees. These rewards encourage miners to spend on the machines and energy that are needed in the process, to maintain the decentralized network we have today.
- Equality of Cryptocurrency: It guarantees that any new currency that has been minted is well distributed within the network due to the effort that a miner has to put in to win the PoW round. This process is less akin to pre-BTCs, where some tokens are given before creating a network of the same type.
Due to its previous successes, it is one of the reliable solutions, which can be used to protect blockchain networks. It makes it increasingly less likely that miners and network participants will seek to undermine a cryptocurrency’s blockchain.
Cryptocurrencies That Use Proof of Work Model

Proof of Work is one of the widely used consensus algorithms with large-scale blockchain applications. Approximately 64% of the total market capitalization of the universe of cryptocurrencies uses proof of work for validation.
While Bitcoin is the most notable example, several other cryptocurrencies also utilize POW:
- Ethereum (Before Ethereum 2.0 Transition): Ethereum used PoW until 2022 even though it was employed to confirm transactions and protect the blockchain. It has since passed that phase to Proof of Stake (PoS) as currently used by Ethereum.
- Litecoin (LTC): It is derived from Bitcoin with the difference in the use of its PoW-Scrypt algorithm is easier and faster than Bitcoin’s SHA-256 and enables miners who do not have sophisticated graphic cards to mine the cryptocurrency due to its faster transaction rate compared to Bitcoin which is often referred to as “the gold of crypto.”
- Monero (XMR): As one of the privacy coins, Monero utilizes PoW with RandomX to ensure decentralization since the consumer can mine cryptocurrencies on their PCs.
- Dogecoin (DOGE): Originally, it was an experimental meme currency. It works with the PoW-Scrypt algorithm. Due to having almost similar mining algorithms, it is also mined alongside Litecoin.
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH): Bitcoin’s Sister, Bitcoin Cash uses this algorithm to determine the most efficient and secure blocks through consensus, as well as solve the scalability problem present in Bitcoin.
Challenges and Limitations of Proof of Work
Proof-of-work systems have attracted criticism for their massive appetite for electric power. Despite its widespread adoption and proven security, PoW has several challenges and limitations:

- Energy Consumption: The most prevalent criticism of proof-of-work is that it wastes energy. Multiple research estimates that Bitcoin uses more energy than several midsized countries. Mining is a highly computational-intensive function, and hence, it consumes much power. For example, someone is concerned about ether’s per-transaction energy consumption, which is similar to that of Bitcoin, an actual small country.
- Hardware Centralization: The PoW approach is now almost entirely aligned with decentralization, and domination has led to bundles of miners with highly advanced hardware such as ASICs( Application-Specific Integrated circuits). This centralization can hold enormous sums of mining power in few hands and thus is against the concept of decentralization, which is the hallmark of cryptocurrencies.
- Scalability Issues: A massive disadvantage of PoW networks is that they scale poorly. Bitcoin, for instance, has a very humble throughput of about 7TPS while Visa processes thousands of TPS. This is a result of the time and effort needed to mine PoW, which is a constraint.
- 51% Attacks: Although this is uncommon for existing digital currencies such as Bitcoin, new PoW networks are frequently at risk of 51% attacks, in which an individual or group obtains the majority of the mining computing power. This control can jeopardize the existence of the coins or allow them to practice double-spend or carry out a hostile takeover on the network.
- Environmental Criticism: The sustainability of PoW has been criticized based on the firm belief that the network has enormous environmental influence. This concern has spurred the creation of other forms of consensus mechanisms such as the proof of stake, to help cut energy consumption.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake: Key Differences Between Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
The two consensus mechanisms typically utilized in blockchain networks are Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. Proof of Work, first cryptocurrency consensus mechanism which is used by early blockchains, established dominance with Bitcoin by using mining.
PoS provides an alternative in which participants are not chosen to win by solving puzzles but are chosen based on the amount of interest they have in the network.
Below are the major differences between the consensus mechanisms:
| Features | Proof of Work | Proof of Stake |
| Energy Consumption | High; requires extensive computation power | Low; relies on staking rather than computing |
| Transaction Speed | Slower, due to the intensive mining process | Faster, minimal competition among validators |
| Hardware Requirements | Specialized pieces of equipment (e.g., ASICs) are essential | Standard devices suffice. No specialized hardware is needed. |
| Environmental Impact | Significant carbon footprint | Eco-friendly, significantly reduced energy usage |
| Vulnerability to Attacks | Resistant to 51% of attacks due to cost of control | Potential for wealth centralization“ but mitigated by slashing rules |
| Decentralization | Risk of centralization from mining pools | Higher potential for decentralization depending on stake distribution |
Real-World Applications of Proof of Work Technology
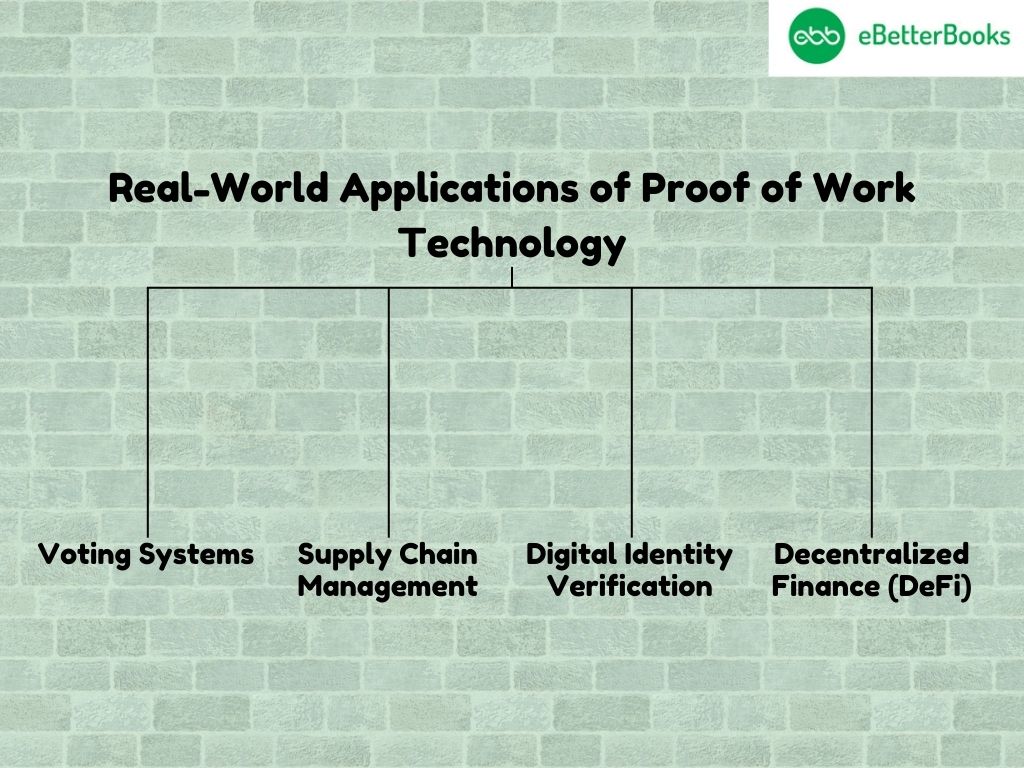
Proof of Work is not limited to securing cryptocurrencies; it has practical applications in other domains. Proof of work technology has been used in various real-world applications, including cryptocurrency mining and blockchain development:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Due to the adequate guarantee of the reliability of the blockchain network, PoW forms the basis of many DeFi platforms. These platforms base the consensus mechanism on PoW for transactions and use smart contracts for unchangeability.
- Digital Identity Verification: In BIS, PoW is used to protect identity records from data alteration and other malicious actions in an identical manner.
- Supply Chain Management: Businesses use PoW-secured blockchains to monitor items while guaranteeing that the data relayed through supply chains is truthful. The development of the PoW reduces transparency and cases of fraud because the ledger is made unalterable.
- Voting Systems: Perhaps PoW can be utilized to generate efficient and secure voting models, guaranteeing that votes will be documented safely and specifically.
Therefore recorded without a central part, these application scenarios show besides the cryptographic applications of PoW, how the mechanism can help to enforce security and transparency in various fields.
Conclusion
Proof of work is the most popular consensus mechanism for validating transactions on blockchains. Miners use proof of work to help ensure that only legitimate transactions are recorded on the blockchain. Therefore, in the future of the proof of work, more specifically, depending on its prospects, it’s necessary to focus on the problems, advantages and disadvantages, such as consumption and the possibility of scaling.
Such technologies as renewable energy in mining and hybrid consensus mechanisms are opening the way to more sustainable uses. Even though PoW can boast of its high level of security and decentralization, the core of the system and negative impact on the environment can act as a bar that hinders the widespread adoption of these technologies in any industry that requires their uniqueness.
Like with most technologies, advancements will start to decrease the relevance of PoW with possibilities like Proof of Stake coming into play. However, due to its basic concepts and achievements in securing networks such as Bitcoin, it will always become an important part of the blockchain story and advancement.
